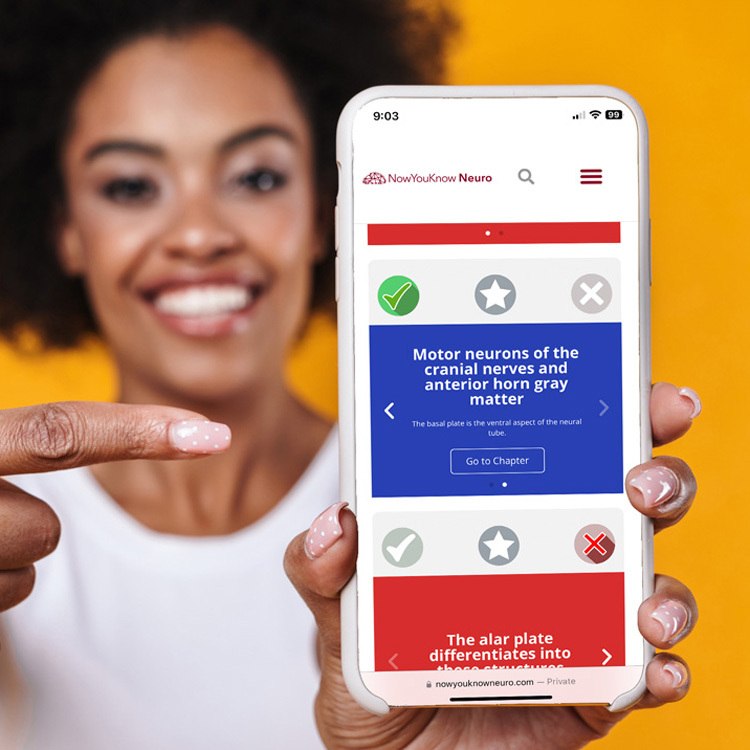
1000+ High-yield flashcards.
Fast and effective studying and last-minute review.
Track your performance.
Included in all NowYouKnowNeuro plans

NowYouKnowNeuro LLC © 2024, all rights reserved
8105 Fayetteville Rd. STE 113-123
Raleigh, NC 27603
Our “Board Pass Guarantee” is designed to provide added confidence and support for users preparing for the ABPN “Initial Certification in Neurology” or ABPN “Continuing Certification in Neurology” examinations. The following terms and conditions apply: