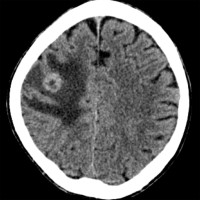
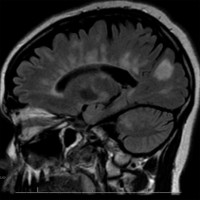
Below you will find over 450 high-yield neuroradiology images, including CT, MRI, and vessel (CTA/MRA) images. These images were selected to be the most valuable for in-service/RITE*, and ABPN board examinations.
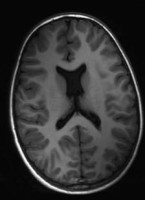
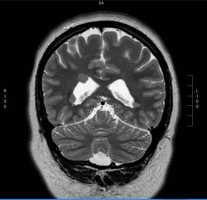
DESH
Axial CT head showing a disproportionately enlarged subarachnoid space and hydrocephalus DESH)
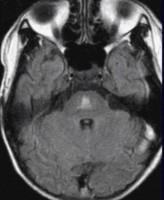
Labeled hypothalamic hamartoma
Coronal T2 (left), T2 FLAIR (middle), and T1-weighted MRI showing hypothalamic hamartoma (arrow).
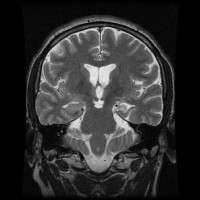
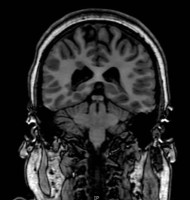
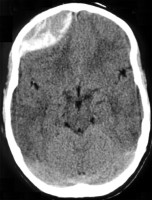
DESH coronal CT
Coronal CT Head showing enlarged subarachnoid spaces
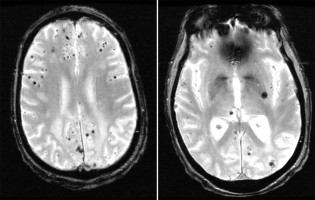
Superficial siderosis axial swan
Axial cut MRI, SWAN sequence showing hemosiderin staining along the sulcal convexities
Wernickes Mammillary body enhancement MRI sagitial
Contrasted sagittal T1-weighted MRI showing enhancement of the mammillary bodies
Wernickes Mammillary body enhancement MRI axial
Contrasted axial T1-weighted MRI showing enhancement of the mammillary bodies (yellow arrow)
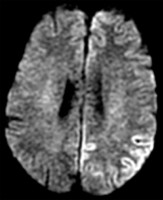
Watershed infarct MRI axial DWI
Axial MRI, DWI sequence showing hyperintensities in the ACA-MCA and MCA-PCA distributions.
VZV encephalitis MRI axial FLAIR
Axial MRI, FLAIR sequence showing hyperintensities in the left mesial temporal lobe
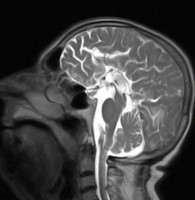
Vein of galen MRI MPRAGE sagittal
Sagittal MRI, MPRAGE sequence
Tumefactive NMO SD MRI T2FLAIR
Axial MRI, T2 sequence
Vein of galen MRA sagital
MRA sagittal cut
Tumefactive NMO SD MRI T1PC
MRI brain, axial T1 sequence with contrast showing lesional contrast enhancement
Tumefactive NMO SD MRI SWI
MRI brain, axial SWI sequence showing hemosiderin deposition
Transverse sinus thrombosis MRV coronal
Coronal MR venogram with right transverse sinus thrombosis
SDH chronic MRI T1-
MRI Brain axial cut, T1 sequence showing bilateral slightly hyperintense extracortical lesions
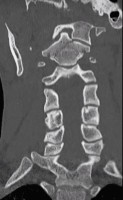
C6-C7 cord compression
Sagittal cervical spine MRI. Note the compression at C6-C7.
MS cervical spine lesion chronic MRI sagital STIR
MRI brain, STIR sequence sagittal cut
LETM MRI sagital STIR
MRI brain, STIR sequence sagittal cut
LETM NMO MRI sagital STIR
MRI brain, STIR sequence sagittal cut
Cervical cord stenosis MRI sagital SITR
MRI c-spine, STIR sequence, sagittal cut
Diffuse spinal glioma sagittal T1-PC
Diffuse spinal glioma sagittal T2
diffuse spinal glioma STIR
spinal cord infarct SAG DWI 2
Sagittal MRI, DWI sequence, showing hyperintensity of the thoracic spinal cord
spinal cord infarct SAG DWI 1
Sagittal MRI, DWI sequence, showing hyperintensity of the thoracic spinal cord
Longitudinally-extensive transverse myelitis (LETM) on sagittal T2 MRI
Sagittal T2 Cervical MRI showing hyperintensity of the spinal cord extending three vertebral levels
L3 L4 herniated disc plus MS lesion
Spinal Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
MRI spine, sagittal view. Large vascular spaces in the extradural space of the lumbar spine are consistent with a lumbar spine AVM.
L4-L5 Disc Herniation
By Jay Moore - Own work, CC0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=27202525
S1 Disc Herniation
By Mjorter at Dutch Wikipedia - Transferred from nl.wikipedia to Commons., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1851539
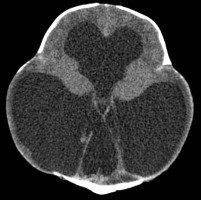
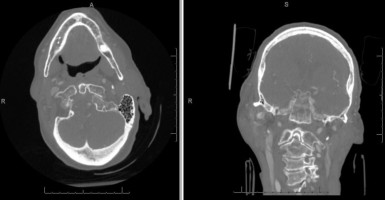
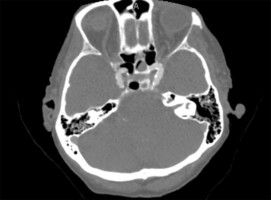
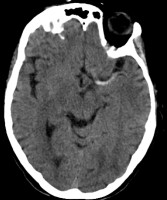
Aqueductal Stenosis
Axial head CT showing severe obstructive hydrocephalus due to aqueductal stenosis.
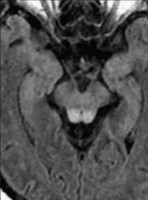
Wernicke's Encephalopathy (WE)
Axial MRI, T2 FLAIR sequence. Hyperintensity within the bilateral midbrain tectum is seen, which is classic of WE.
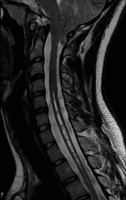
Spinal Syrinx and Chiari Malformation
Sagittal T2-weighted cervical spine MRI. Note the cavity within the cord that is isointense relative to the CSF. Syringomyelia (syrinx) is sometimes seen alongside Type 1 Chiari malformation.
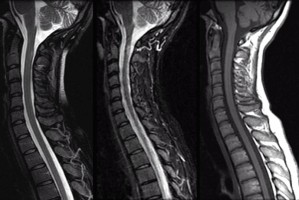
Multiple Sclerosis
Left: Sagittal spine MRI, T1 sequence. Middle: T1 w/ contrast. Right: T2. Note the contrast-enhancing cervical lesion, consistent with an active plaque.
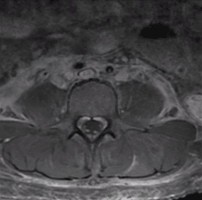
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
Axial spine MRI with contrast. Note the contrast enhancement of the cauda equina and nerve roots.
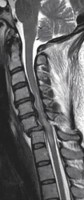
Spinal Cord Contusion
MRI cervical spine, sagittal view. The contusion is secondary to cervical spine fracture.
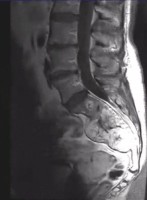
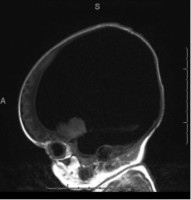
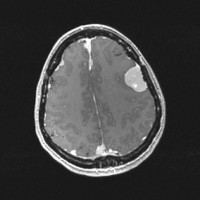
Lumbar spine MRI showing a destructive sacrococcygeal lesion suggestive of chordoma
Lumbar spine MRI, sagittal view.
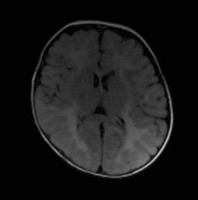
Adrenoleukodystrophy
Axial T2 FLAIR MRI showing posterior-predominant white matter hyperintensities consistent with adrenoleukodystrophy.
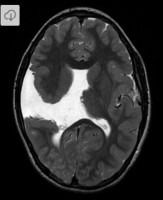
Schizencephaly
Axial MRI, T2 FLAIR, showing open-lipped (Type 2) schizencephaly with unfused edges and exposure to the subarachnoid space.
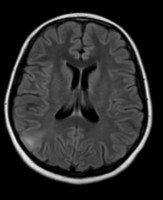
Focal Cortical Dysplasia
Axial T2 FLAIR MRI showing focal hyperintensity of the right parietal cortex.
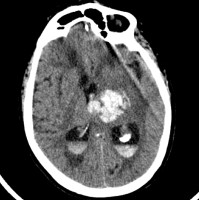
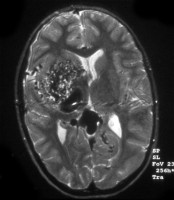
Intracerebral Hemorrhage of Left Thalamus
This was secondary to hypertension. Note the intraventricular spread.
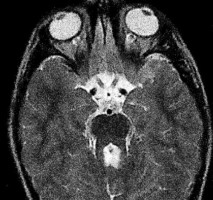
Hereditary and Metabolic Disorders Discussion: This clinical picture describes a typical presentation and MRI findings of Joubert syndrome; in which there is hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis. The most common features of this syndrome include hyperpnea, hypotonia, oculomotor apraxia, ataxia, and intellectual disability. Other neurologic manifestations include seizures. The molar tooth sign, which is the result of the thickening and horizontalization of the superior cerebellar peduncle and a deep interpeduncular fossa, can also be seen in several other disorders including Dekaban-Arima syndrome, Senior-Loken syndrome, and COACH (cerebellar vermis hypoplasia, oligophrenia, ataxia, coloboma, and hepatic fibrosis).
Hereditary and Metabolic Disorders
Discussion:
This clinical picture describes a typical presentation and MRI findings of Joubert syndrome; in which there is hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis. The most common features of this syndrome include hyperpnea, hypotonia, oculomotor apraxia, ataxia, and intellectual disability. Other neurologic manifestations include seizures. The molar tooth sign, which is the result of the thickening and horizontalization of the superior cerebellar peduncle and a deep interpeduncular fossa, can also be seen in several other disorders including Dekaban-Arima syndrome, Senior-Loken syndrome, and COACH (cerebellar vermis hypoplasia, oligophrenia, ataxia, coloboma, and hepatic fibrosis).
Log in to View the Remaining 60-90% of Page Content!
New here? Get started!
(Or, click here to learn about our institution/group pricing)1 Month Plan
Full Access Subscription
$142.49
$
94
99
1 Month -
Access to full question bank
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to all chapters & site content
3 Month Plan
Full Access Subscription
$224.98
$
144
97
3 Months -
Access to full question bank
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to all chapters & site content
1 Year Plan
Full Access Subscription
$538.47
$
338
98
1 Year -
Access to full question bank
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to all chapters & site content
Popular